The best way to train fat metabolism
For endurance athletes, whether beginners or ambitious, the following applies: athletic performance depends strongly on the energy metabolism and its characteristics. Fatty acids and carbohydrates serve as energy suppliers for this purpose. While carbohydrate stores are only very limited, we can make use of fats as an energy source for a very long time. The longer and more intense the endurance exertion, the more important the availability of energy and the corresponding supply of energy to the working muscles. Thus, fat metabolism becomes an essential factor for your endurance performance. With the help of this article, you will learn to understand the physiology of the body and get the necessary tools to effectively burn more fat and be more efficient in the future.

What is fat burning? And how is it regulated in the body?
Every form of work requires the release of energy, including the body's processes. This energy is released by the cleavage of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and phosphate (P). However, we are faced with the following problem: In our body, we only have a small amount of ATP stored, which is just enough for one to three muscle contractions. Luckily, the human organism is so damn clever and developed. To ensure the additional consumption of ATP, the body resorts to three types of ATP resynthesis:
1: anaerobic-alactacid ATP resynthesis
2: the anaerobic-lactacid ATP resynthesis.
3: the aerobic (oxidative) ATP resynthesis
 Anaerobic energy production takes place without oxygen (an= "without" and aer= "air") and takes place outside the mitochondria (the power plants of the cells). A distinction is made here as to whether increased lactate is formed (alactacide) or whether the lactate concentrations remain unchanged (alactacide).
Anaerobic energy production takes place without oxygen (an= "without" and aer= "air") and takes place outside the mitochondria (the power plants of the cells). A distinction is made here as to whether increased lactate is formed (alactacide) or whether the lactate concentrations remain unchanged (alactacide).
Aerobic energy supply takes place in the mitochondria. Here, glycogen and fats are broken down with the participation of oxygen to resynthesize ATP. Carbohydrates are stored in the form of glycogen, while fat is stored in the form of triglycerides. A triglyceride consists of 3 fatty acids. These fatty acids, which must first be broken down, serve as the fuel for aerobic energy production.
Both aerobic and anaerobic energy supply(s) have advantages and disadvantages. Which system the body resorts to depends primarily on the intensity of the load and the associated rate of energy flow per unit of time. If a lot of energy is needed in a short time, for example during a sprint or an attack, the body resorts to anaerobic energy metabolism. This involves greater or exclusive use of carbohydrates because their energy can be released much more quickly and easily than that of fat - and without much oxygen. Fat, on the other hand, is preferred for "lower" intensity exercise because it requires a lot of oxygen and less energy per unit of time.
Why is this critical for me as an endurance athlete?
In long-term endurance events such as marathons or triathlons in general, energy availability, as well as fuel management, takes on a crucial role.
Depending on the athlete, the glycogen stored in the muscles and liver can easily store about 2000kcal (500g) of carbohydrates in the body. This may seem like a lot at first glance, but it is possible to use them up completely at a high intensity between 90 and 120 minutes. As a result, you will have to replenish these stores after the training/competition, or even during it. This is exactly why the importance of fat metabolism increases with the duration of the load.
Because fat in turn has a high energy density, of which we also have a lot stored in our body. One could think we have unlimited storage available because even an 80-kilo runner with 10% body fat has 56,000kcal available in his body as an energy supply!
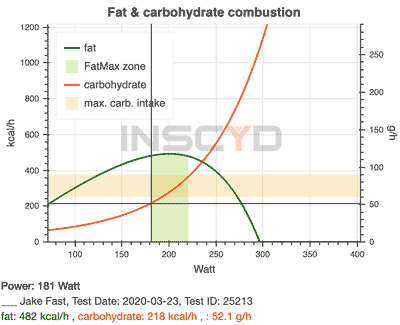
It is important to understand that in principle it is always a "juxtaposition" and not a "succession" of the individual energy supplies. Rather, it is a shifting and overlapping transition of the different systems depending on the load intensity. So there is a change in the mix of fat and carbohydrates you need for your activity, depending on the relative intensity. At "lower" intensity, you consume proportionally more fat, but also carbohydrates. As intensity increases, you consume more carbohydrates, but less to no fat.
In addition to the duration and intensity of the load, the training condition of the athlete is also involved in the proportion of energy supply. The more trained, the higher the proportion of fatty acid combustion in the energy supply and the longer the muscles can manage the valuable glycogen reserves.
What are the best methods to train and improve fat metabolism in the long term?
|
We would like to provide you with several methods. For this, we will go into three common methods from the nutrition and training practice.
- One method that is probably familiar to most and has been used for a long time is fasting training. Here, breakfast is usually dispensed in the morning, and only water, unsweetened tea, or coffee is drunk before the start of the workout. This is followed by a relatively short workout of 30-60 minutes in the basic range, during which no further energy is supplied.
- A similar variant is low-carb training. Here, you can have breakfast before the start of the workout, but limit the food selection to protein and fat-rich foods. For example, your breakfast could consist of an omelet with vegetables or cottage cheese with a portion of nuts. This is followed by another base workout, which can be a bit longer and can also take place in the upper range of the base workout.
Important: It is better to start a little more conservatively, both in terms of length and intensity of training. Also, we recommend that you always have an emergency or other sugar with you. Furthermore, do not start training every day sober or low-carb, and not for a long period. This type of training also causes a lot of stress in the body and puts a strain on the immune system. Also, for women, who may well be more sensitive to this type of training, these two methods should be used sparingly. - Again and again, one hears about the ketogenic diet, i.e., a form of nutrition that relies almost exclusively on proteins and fats in the diet. In short, there is no consistent evidence that the ketogenic diet is superior to the classic high-carbohydrate diet. On the contrary. Nevertheless, you should not necessarily eat carbohydrates 1h before a session that aims to use more fats as an energy source. The body is very clever and would in this case rely more on them because they are easier and faster available than getting energy from the breakdown of fats. IMPORTANT: Before high-intensity sessions, you should ensure that you have taken in enough carbohydrates beforehand.
- Another classic training method is the long ride or long run. These also usually take place in the GA1 - Fat-max range.
- As a supplement to the fourth method, you can incorporate short sprints, with a duration of 6-8 seconds and a subsequent break of 8-10 minutes. You can integrate these wonderfully into a 1.5-2 hour basic ride. This could look like this:
- 20 min Zone 2, 10x 6-8sec. Sprints with 8 min Zone 2 in between, 20 min Ga1 out.
- 2x training/day: Here, especially in the second training unit, increased use is made of the fat metabolism, since in the first unit the glycogen stores were already partially emptied. This effect can be intensified if after the first unit only limited or no carbohydrates are supplied. IMPORTANT: You should still absolutely supply proteins + carbohydrates after a high-intensity unit!

Conclusion - The best way to train fat metabolism
Whether triathlon, running, cycling, or swimming…. You should definitely strive to train your fat metabolism to improve your endurance performance in the long term. You will benefit not only in training, but especially in competition. We have explained how you can best trigger your fat metabolism using various methods. It is best to combine these methods and carefully approach the nutrition strategies. Keep the intensities (Fat-max) in mind and be patient with the development of the fat metabolism.
 EN
EN  DE
DE 
 First, it should be said that fat metabolism can not be improved overnight. The development of the upstairs metabolism takes a long time and, in the end, never stops.
First, it should be said that fat metabolism can not be improved overnight. The development of the upstairs metabolism takes a long time and, in the end, never stops. 









